python-fall-2022
google meet link: https://meet.google.com/umh-pgbg-mny

Note:
- the next APCS exam is on 1/08. The class has been rescheduled for 12/25 from 13:30-15:30.
12-18-2022
Continue working on Final Projects
JSON example here
Platformer state machine example here
12-11-2022
Design and start implementing final projects
A separate repository for final project notes is here: https://github.com/cmorace/PeanutsPythonFinalProject
Eric: CandyCats Repository
Feng-Jun: MailModel Repository
12-04-2022
Intro to OpenCV
Example 0. Check OpenCV version
import cv2 as cv
print("OpenCV version:", cv.__version__)
Example 1. Load, Save, and View an Image
import cv2 as cv
import sys
img = cv.imread("images/baboon.bmp")
if img is None:
sys.exit("Could not read the image.")
cv.imshow("Display window", img)
k = cv.waitKey(0)
if k == ord("s"):
cv.imwrite("saved_cv_image.png", img)
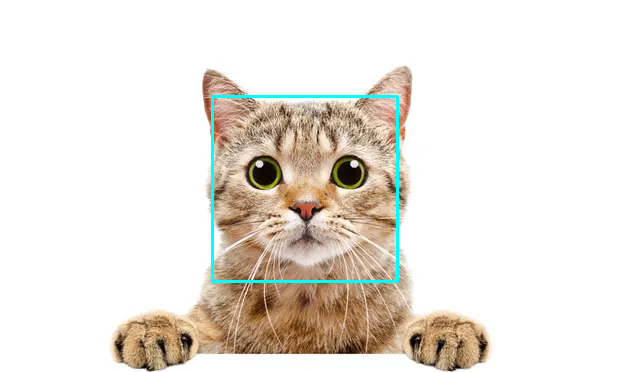
Example 2. Detect a cat’s face in an image
import cv2 as cv
print("OpenCV version:", cv.__version__)
cascade = cv.CascadeClassifier('cat_face_extended.xml')
img = cv.imread("01_cat.webp")
img_gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cats = cascade.detectMultiScale(img_gray, scaleFactor=1.05, minNeighbors=4)
print(len(cats), "cat faces detected")
for (x, y, w, h) in cats:
cv.rectangle(img, pt1=(x, y), pt2=(x+w, y+h),
color=(255, 255, 0), thickness=2)
Download the cascade classifier XML file from here
Exercise:
View and save the image showing the detected cat’s face. If faces are not detected, tune the parameters for scaleFactor and minNeighbors.
Extension:
Download other cascade classifiers from here and detect other objects in an image.
Additional Resources
11-27-2022
Review:
try/except,Exceptions- sockets
conn, addr = socket.accept()conn.sendto(sent_message.encode(), addr)received_message = str(conn.recv(1024), encoding='utf-8')conn.close()
- threads
thread = Thread(target=foo, args=(a,b,))thread.start()
Python
- implement a multi-threaded server
Main Thread ------------ set is_waiting_for_connection = False while True if not is_waiting_for_connection: start thread to receive a connection for each connection if connection is not waiting for message start a new receiving thread Receive Connection Thread --------------------------- set is_waiting_for_connection = True when receive new connection: add connection to list of connections send back acknowledgment to cliet set is_waiting_for_connection = False Receive Message Thread (every connection has a seperate thread) ------------------------- set connection_is_waiting = True try to get a new message receive message set connection_is_waiting = False send acknowledgement back to client except error close connection close connection remove connection from list of connections - introduce multiprocessing module
- test out OpenCV, image loading, face detection
- finish C and Linux lesson from last week
11-20-2022
Python Lesson
-
Set up two client windows and one server window and test.
-
Review Reference socket
a.
socket.sendall()vs.socket.sendto()vs.socket.send()b.
socket.accept() -
Review
try/exceptdetails. Reference: errors -
Implement
try/exceptin server.py -
Design and implement a state machine for the server.
a. Clean up the code. Make Server a class.
-
Introduce multi-threading. Reference threading
-
Implement multi-threading in server.py
C Lesson
-
types, arrays, pointers,
sizeof -
example of pass-by-value, pass-by-reference, and pass-by-pointer
Linux Lesson
-
using the apt package manager
-
introduce Bash scripting
-
introduce GNU make
Homework: Study ‘The C Programming Language’ book and review Linux references
11-13-2022
Check-in
Is docker-desktop still not working? It would be nice to work in the same environment if possible.
Last week our environments for practicing Linux and C
- Teacher using macOS or Ubuntu with Docker
- Feng-Jun using Ubuntu with WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux)
- Eric is using git-bash and downloaded MinGW
Mini Linux(Bash) Lesson
The ~/.bashrc file
Aliases
alias update-pycat="pip install git+https://bitbucket.org/dwhite0/pycat.git -U"
alias python-class="code <your absolute workspace path>"
alias bashrc="code ~/.bashrc"
alias gcc="<path to gcc.exe>" # for windows
Export Path variable
export PATH="<bin directory>:$PATH"
Mini C Lesson
Check your C compiler
gcc --version
Write two functions in C
- convert from degrees to radians
- convert from radians to degrees
Compile with gcc
Python Lesson
Server
import socket
HOST = '127.0.0.1'
PORT = 8000
server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
server.bind((HOST, PORT))
server.listen(10)
conn, addr = server.accept() # wait until get a message
serverMessage = 'connected to client'
conn.sendall(serverMessage.encode())
while True:
clientMessage = str(conn.recv(1024), encoding='utf-8')
print('Client message is:', clientMessage)
serverMessage = 'I\'m here!'
conn.sendall(serverMessage.encode())
Client
import socket
from pycat.core import Window, Sprite
HOST = '127.0.0.1'
PORT = 8000
clientMessage = 'Hello!'
client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
client.connect((HOST, PORT))
w = Window(200, 200)
class Button(Sprite):
def on_create(self):
self.scale = 100
self.position = w.center
def on_left_click(self):
print("sending to server")
client.sendall(clientMessage.encode())
serverMessage = str(client.recv(1024), encoding='utf-8')
print('Server:', serverMessage)
w.create_sprite(Button)
w.run()
- Make sure we can connect and send messages from client to server with pycat
- Introduce keywords
try/except - Decompose the two-player online game problem
- Design a simplified Server state machine for two player game
- Design a simplified Client state machine for two player game
Can we design a reusable module for a two-player server-client model?
Homework
- Brainstorm ideas for your final project. The more ideas, the better.
- Continue work on the two-player asteroid game.
- Study python reference material for multiprocessing and socket
- Work on previous exam’s APCS problems.
- Study and test some code from The C Programming Language book
Lesson 2: 2022-11-06
APCS questions
My solutions are in the repository. I recommend trying your best to solve them on your own before looking. Note: the solution to question 4 exceeds the time limit for most test cases on ZeroJudge.
Getting Started with Linux
Linux is an open-source operating system with many distributions to choose from, e.g., Ubuntu, Debian, Red Hat, ArchLinux, CentOS, etc.
There are a few different options for running Linux distributions.
-
Installing a new operating system on your pc is risky and time-consuming. If anything goes wrong, you might have to reinstall. Don’t do this unless you have a lot of experience debugging installation and hardware problems with Linux.
-
Dual-boot: Partition your hard drive and install Linux on one of the partitions. One partition runs your current O.S., and the other runs a Linux distribution. Also time-consuming. Less risky than option 1. but requires some experience with Linux and partitioning your disk.
-
Use a virtual machine. We have done this in the past with the APCS environment. A virtual machine is a very safe option but requires some knowledge of the virtualization software, e.g., VirtualBox. Performance is limited.
-
Use a development container with Docker, the safest and easiest method, but you only have access to a shell environment. There is no GUI. Performance is usually better than running a virtual machine. Containers make it easy to set up, test quickly, and deploy different development environments but require some knowledge of Docker.
Setting up Docker and Dev-Containers
- Install Docker
- Install the Dev-Containers Extension
A mini Unix Shell lesson
create a file with the touch <filename> command
delete a file with rm <filename>
create a directory with mkdir <dirname>
navigate the filesystem with cd
print the working directory with the command pwd
show the contents of a file with the commands cat, head, and tail
show the contents of a directory with ls
how to use help
Server-Client Example
Server
import socket
HOST = '127.0.0.1'
PORT = 8000
server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
server.bind((HOST, PORT))
server.listen(10)
while True:
conn, addr = server.accept()
clientMessage = str(conn.recv(1024), encoding='utf-8')
print('Client message is:', clientMessage)
serverMessage = 'I\'m here!'
conn.sendall(serverMessage.encode())
conn.close()
Client
import socket
HOST = '127.0.0.1'
PORT = 8000
clientMessage = 'Hello!'
client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
client.connect((HOST, PORT))
client.sendall(clientMessage.encode())
serverMessage = str(client.recv(1024), encoding='utf-8')
print('Server:', serverMessage)
client.close()
Lesson 1: 2022-10-30
-
Discuss the future of our class
a. Independent Project-Based (self-directed) vs. Planned Lesson (teacher-led)
b. More APCS practice/homework?
c. New directions? C/C++, Unity, Web Programming, 3D Graphics, Computer Vision, Machine Learning, Visualization, Operating Systems/Multi-threading/interprocess-communication, etc.
-
Today’s lesson
a. Look at new pycat projects
-
Asteroids
-
GeoGuesser
-
Animal Crossings
b. Choose a project and start working on it
-
Discussion
-
Start with planned lessons
-
Add some C programming
-
Add some multiprocess lessons (server/client). Maybe turn Asteroids into a remote two-player game?
-
Add some Linux (Feng-Jun)
-
-
Do an independent project
-
Continue some APCS (more APCS content closer to the next test date, 2023-01-08)
Homework (choose one)
-
Look at the most recent APCS problems https://yuihuang.com/apcs/. Then, work on the solutions and submit them to ZeroJudge. Review questions next class.
-
Continue working on your current Asteroids game.
-
Research/Design a two-player asteroid game.
a. Two computers with different IP addresses (two clients). One server synchronizes data between the two clients. Therefore, we need two programs, one for the client and another for the server.
b. Draw a diagram with the clients and server. What messages need to be sent and received for the game to work?
c. Draw one state-transition diagram for the server application and another for the client applications.
d. Explain your diagrams in the next class.
e. Research what python functions can send/receive data between multiple processes?
Install and/or update pycat
pip install git+https://bitbucket.org/dwhite0/pycat.git -U
clone pycat repo (optional)
git clone git@bitbucket.org:dwhite0/pycat.git